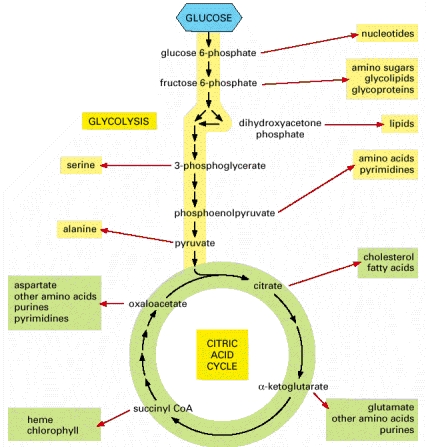
- The production of ATP initial requires glucose to be converted into two pyruvate molecules. This reaction is known as glycolysis and occurs in the cytosol of the cell outside the mitochondria. Each pyruvate molecule generates one ATP and another activated carrier molecule known as NADH.
- The pyruvate then passes from the cells cytosol into the mitochondria. Where it is converted into carbon dioxide and acetyl CoA, which is another activated carrier molecule.
- Acetyl CoA can also be produced by the oxidation of fatty acids derived from fats.
- The acetyl group in acetyl CoA is then oxidised to generate CO2 (carbon dioxide) and large amounts of NADH via the citric acid cycle. This stage occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- The NADH molecules carry high-energy electrons, which are then passed along an electron-transport chain, a process known as oxidative phosphorylation. This stage occurs within the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- The energy released by the transfer of the high-energy electrons is used to drive the ATP synthesis, which also requires oxygen. In these final oxidization steps, the majority of the energy generated is used to produce most of the cells energy.
Image courtesy of
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=mboc4&part=A163#A304